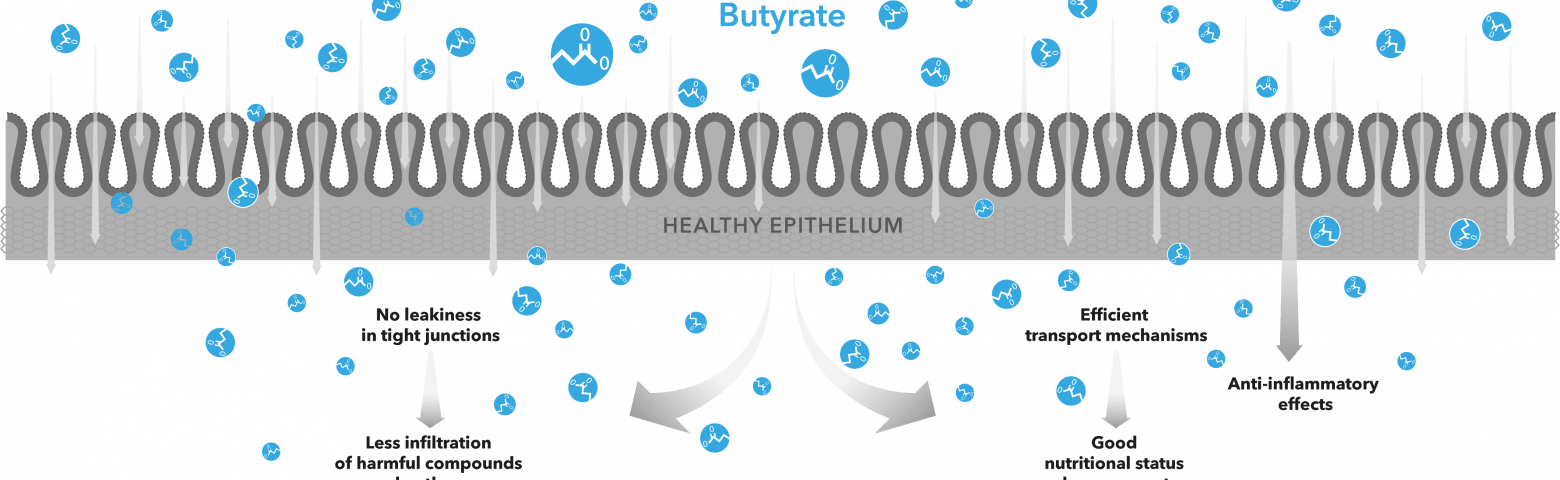
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) of 4-carbon atoms, is generally considered to be the preferred energy source of epithelial cells in the large intestine. Once produced by bacterial metabolism in the intestinal lumen, much of the butyrate is absorbed, to benefit the host animal’s energy status.